What is the Keto Diet?
The Keto Diet, short for the ketogenic diet, is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate eating plan popular for its effectiveness in weight loss and health improvement. By significantly reducing carbohydrate intake and replacing it with fats, the body enters a state called ketosis, where it burns fat for energy instead of carbohydrates. This metabolic shift can lead to various benefits, including reduced hunger, increased fat burning, and improved energy levels, making it an attractive option for many seeking to lose weight and enhance their health.
History of the Keto Diet
The ketogenic diet was originally developed in the 1920s as a therapeutic intervention for epilepsy in children, aiming to reduce the frequency of seizures. The diet is characterized by a high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate intake, which leads the body to enter a state of ketosis, where it burns fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates.
Over the years, the benefits of the ketogenic diet have expanded beyond epilepsy, gaining recognition for its potential in weight loss, improved metabolic health, and increased energy levels. As research continues, many individuals are adopting the ketogenic diet as a lifestyle choice for enhanced health and well-being, contributing to its widespread popularity today.
How the Keto Diet Works
Ketosis Explained
Ketosis is a metabolic state in which the body uses fat as its primary energy source instead of glucose from carbohydrates. When carb intake is significantly reduced, the liver converts fat into ketones, which fuel the body.
Benefits of Ketosis
Entering ketosis has numerous benefits, including rapid weight loss, increased energy, and improved mental clarity. It also helps stabilize blood sugar levels, making it a good option for those with insulin resistance or diabetes.
Health Benefits of the Keto Diet
Weight Loss
The keto diet is indeed highly effective for weight loss, primarily due to its unique metabolic approach. When the body enters a state of ketosis by drastically reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing fat consumption, it begins to burn fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. This switch to a fat-burning state allows the body to efficiently utilize stored fat as energy, leading to significant weight loss.

Additionally, several factors contribute to the effectiveness of the keto diet for weight management:
- Appetite Suppression: Many people find that high-fat and moderate-protein foods are more satiating, which can lead to reduced hunger and calorie intake.
- Stabilized Blood Sugar Levels: By minimizing carbohydrate intake, the keto diet helps stabilize blood sugar levels, reducing insulin spikes that can lead to cravings and overeating.
- Increased Fat Oxidation: In ketosis, the body increases its reliance on fat as an energy source, which can accelerate fat loss, especially in those with higher body fat percentages.
- Reduced Water Weight: Initially, individuals may lose some weight due to the body’s depletion of glycogen stores and the associated water loss. This can be motivating and kickstart further weight loss efforts.
- Enhanced Energy Levels: As the body becomes adapted to burning fat for fuel, many people report improved energy levels and mental clarity, which can help maintain an active lifestyle.
It’s important to approach the keto diet with careful planning to ensure balanced nutrition and to consult with a healthcare provider or nutritionist, especially for individuals with underlying health conditions. Overall, the keto diet can be a highly effective tool for weight loss and improved metabolic health when followed sustainably.
Improved Mental Clarity
Many people report improved focus and mental clarity while in ketosis because ketones serve as a more efficient fuel source for the brain compared to glucose. This switch leads to:

- Stable Energy Levels: Ketosis minimizes blood sugar fluctuations, preventing energy crashes and brain fog.
- Neuroprotective Effects: Ketones may have protective properties that enhance cognitive function and reduce neuroinflammation.
- Increased BDNF: Higher levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) can support brain health and improve mood.
- Reduced Inflammation: Lower inflammation contributes to better cognitive function and a lower risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Overall, many individuals enjoy heightened clarity and focus as their bodies adapt to using fat for fuel.
Enhanced Energy Levels
Individuals on the keto diet often experience more consistent and sustained energy throughout the day due to the following reasons:

- Stable Energy Source: Fats provide a more stable energy source than carbohydrates, leading to fewer energy spikes and crashes.
- Ketones as Fuel: In ketosis, the body uses ketones for energy, which can result in a more constant supply of fuel for both the brain and body.
- Reduced Hunger: The high-fat content of the diet tends to promote satiety, helping to reduce the frequency and intensity of hunger, allowing for more even energy levels.
- Enhanced Fat Oxidation: The body becomes efficient at burning stored fat for fuel, ensuring a steady release of energy.
Overall, this stable energy supply contributes to increased endurance and focus throughout the day, making it easier to maintain productivity and activity levels.
Better Blood Sugar Control
The keto diet effectively regulates blood sugar levels by reducing carbohydrate intake, which helps minimize spikes and crashes typical of high-carb diets. Key benefits include:

- Lower Sugar Intake: Less glucose enters the bloodstream, leading to steadier blood sugar levels.
- Stable Insulin Levels: Reduced carbs result in lower insulin production, preventing energy fluctuations.
- Fat as Fuel: The body relies on fat and ketones, which stabilizes energy levels.
- Fewer Cravings: Stable blood sugar reduces cravings for sugary and high-carb foods.
Overall, this contributes to improved metabolic health and lowers the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Keto Diet Foods
Foods to Eat
- Meats (beef, pork, chicken)
- Fatty fish (salmon, trout, mackerel)
- Eggs
- Dairy (cheese, butter, cream)
- Nuts and seeds
- Healthy oils (olive oil, coconut oil, avocado oil)
- Low-carb vegetables (leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower)
Foods to Avoid
- Sugary foods (soda, candy, desserts)
- Grains (wheat, rice, pasta)
- Starchy vegetables (potatoes, corn)
- Fruits (except small portions of berries)
- Legumes (beans, lentils)
- Unhealthy fats (trans fats, processed oils)
Creating Your Keto Meal Plan
Setting Your Goals
When starting the keto diet, it’s important to identify your goals, such as:
- Weight Loss: To shed excess pounds by promoting fat burning.
- Improved Energy: To achieve consistent energy levels without spikes and crashes.
- Better Blood Sugar Control: To stabilize blood sugar levels, especially for those with insulin resistance or diabetes.
- Enhanced Mental Clarity: To improve focus and cognitive function using ketones for fuel.
- Reduced Hunger: To decrease cravings and increase satiety from higher fat intake.
- Athletic Performance: To enhance endurance by improving fat oxidation.
Clarifying your objectives will help tailor your keto approach for optimal results.
Calculating Your Macros
To determine your ideal macronutrient ratio for the keto diet, use a keto calculator to follow these steps:
- Enter Your Information: Input details like age, sex, weight, height, activity level, and goals.
- Calculate TDEE: The calculator will estimate your total daily energy expenditure.
- Get Macronutrient Recommendations: Typically, the breakdown is around:
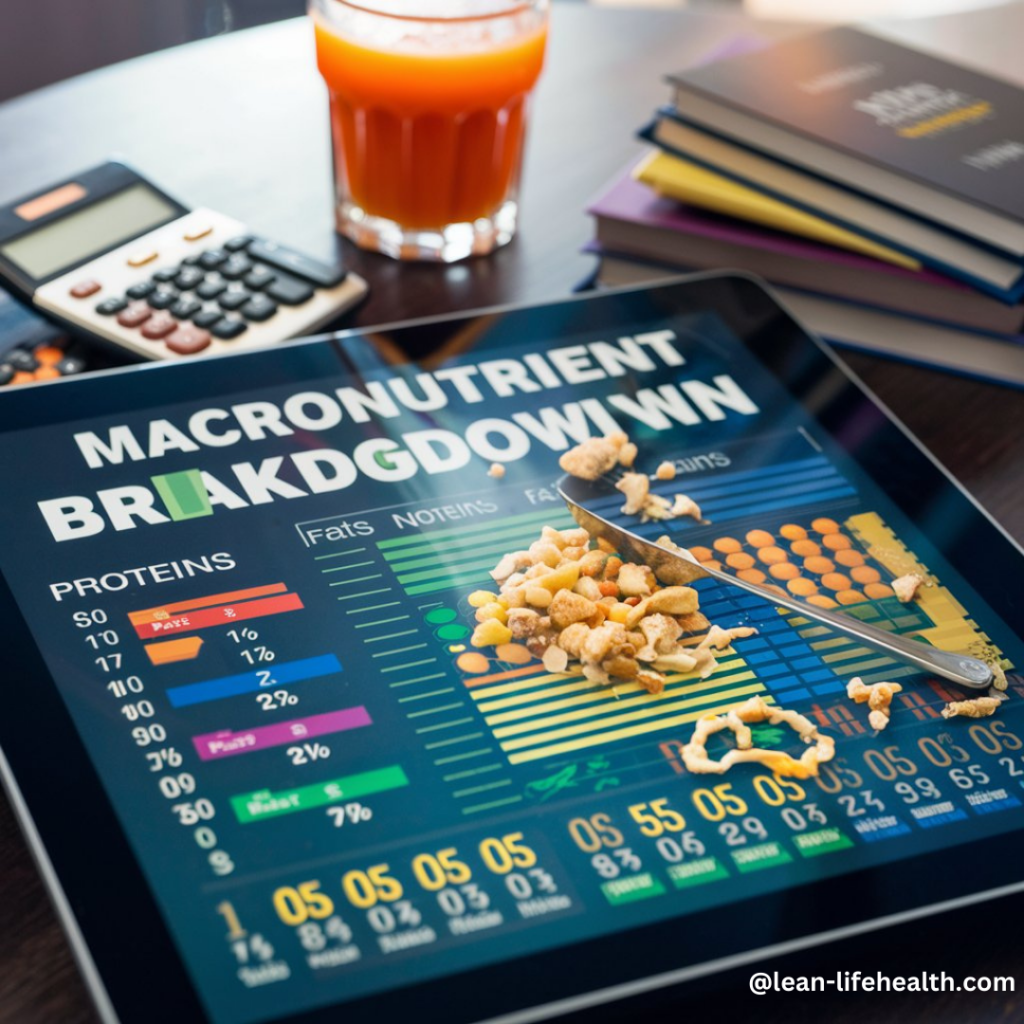

- 70% Fats
- 25% Protein
- 5% Carbohydrates
This will help you customize your intake to align with your health objectives.
Sample Meal Plan
Breakfast
- Scrambled eggs with avocado
- Keto smoothie with coconut milk and spinach
Lunch
- Grilled chicken salad with olive oil dressing
- Zucchini noodles with pesto and parmesan
Dinner
- Baked salmon with asparagus
- Beef stir-fry with bell peppers
Snacks
- Cheese sticks
- Nuts and seeds
- Keto fat bombs
Keto Recipes for Beginners
Breakfast Recipes
- Keto Pancakes: Made with almond flour and cream cheese.
- Bacon and Eggs: A classic, easy, and filling breakfast.
Lunch Recipes
- Keto Caesar Salad: Romaine lettuce, parmesan cheese, and a creamy dressing.
- Lettuce Wrap Tacos: Ground beef, cheese, and avocado wrapped in lettuce leaves.
Dinner Recipes
- Keto Chicken Alfredo: Chicken breast with a creamy, low-carb Alfredo sauce.
- Zucchini Lasagna: Layers of zucchini, cheese, and meat sauce.
Snack Recipes
- Avocado Deviled Eggs: Hard-boiled eggs filled with avocado and spices.
- Keto Trail Mix: A mix of nuts, seeds, and dark chocolate.
Tips for Success on the Keto Diet
Staying Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water is essential on the keto diet for several reasons:
- Hydration: Staying hydrated is crucial for overall health, especially as the body adjusts to a lower carbohydrate intake.
- Metabolism Support: Adequate water intake aids in metabolic processes, helping the body efficiently break down fats and proteins.
- Electrolyte Balance: The keto diet can lead to a loss of electrolytes, so drinking water helps maintain balance and prevents dehydration.
- Appetite Control: Drinking water can help control hunger and reduce calorie intake, making it easier to stick to your dietary goals.

Aim for at least 8 cups (about 2 liters) of water daily, or more if you’re active or in a hot climate. Keeping a water bottle handy can help you remember to drink throughout the day!
Managing Electrolytes
To prevent electrolyte imbalances on a keto diet, consume foods rich in electrolytes, such as:

- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard (high in potassium and magnesium).
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, cashews, and pumpkin seeds (rich in magnesium).
- Avocado: Packed with potassium and healthy fats.
- Broccoli: Contains potassium and essential vitamins.
Tips:
- Add salt to your meals for sodium.
- Stay hydrated with plenty of water.
- Monitor for symptoms like cramping or fatigue.
Incorporating these foods can help maintain your electrolyte balance and overall health!
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
To stay on track with a keto diet, consider these tips for meal prep and avoiding hidden carbs:
Meal Prep Tips:
- Plan Ahead: Create a weekly meal plan with low-carb foods.
- Batch Cook: Prepare large portions of keto-friendly meals to have ready.
- Use Containers: Invest in meal prep containers for easy storage.
- Prepare Snacks: Portion low-carb snacks like nuts and cheese in advance.
- Freeze Meals: Freeze dishes to have quick options on hand.
Avoiding Hidden Carbs:
- Read Labels: Check nutrition labels for hidden sugars and carbs.
- Choose Whole Foods: Focus on unprocessed foods like meats, vegetables, and nuts.
- Be Wary of Sauces: Opt for homemade sauces to avoid added sugars.
- Educate Yourself: Learn which foods can have unexpected carb content.
By prepping meals and being cautious with processed foods, you can better stick to your keto diet!
Exercise and the Keto Diet
Best Exercises to Complement Keto

Incorporate both cardio and strength training to maximize fat loss and muscle gain.
Adjusting Workouts During Adaptation
Allow your body time to adapt to ketosis before engaging in high-intensity workouts to optimize performance. Here are key points:
Adaptation Period:
- Keto Flu: Expect symptoms like fatigue and headaches as your body transitions (usually lasts a few days to a week).
- Energy Levels: Give yourself 2-4 weeks to adapt before doing high-intensity workouts.
Recommendations:
- Start Slow: Begin with low to moderate-intensity exercises during the adaptation phase.
- Listen to Your Body: Adjust intensity based on how you feel.
- Stay Hydrated: Maintain hydration and electrolyte balance.
- Gradual Progression: Increase workout intensity gradually after adapting.
By doing this, you enhance your fitness results and overall well-being!
Potential Side Effects and How to Manage Them
Keto Flu
The keto flu is a common side effect when starting the diet. Combat it by staying hydrated and consuming enough electrolytes.
Tips to Combat Keto Flu:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to prevent dehydration, which can worsen symptoms.
- Consume Electrolytes:
- Sodium: Add salt to your meals or consider broth to boost sodium levels.
- Potassium: Include foods like avocados, spinach, and nuts to help maintain potassium levels.
- Magnesium: Consume magnesium-rich foods such as nuts, seeds, and leafy greens.
- Increase Fat Intake: Ensure you are consuming enough healthy fats to provide your body with sufficient energy.
- Gradual Transition: If possible, gradually reduce carbohydrate intake rather than eliminating them all at once, easing your body into ketosis.
- Rest and Recover: Ensure you get adequate sleep and rest, as your body is adjusting to the new diet.
Digestive Issues
Increasing your fiber intake with low-carb vegetables is an effective way to prevent constipation while following a ketogenic diet. Here are some tips to do this:
Low-Carb Vegetables High in Fiber:
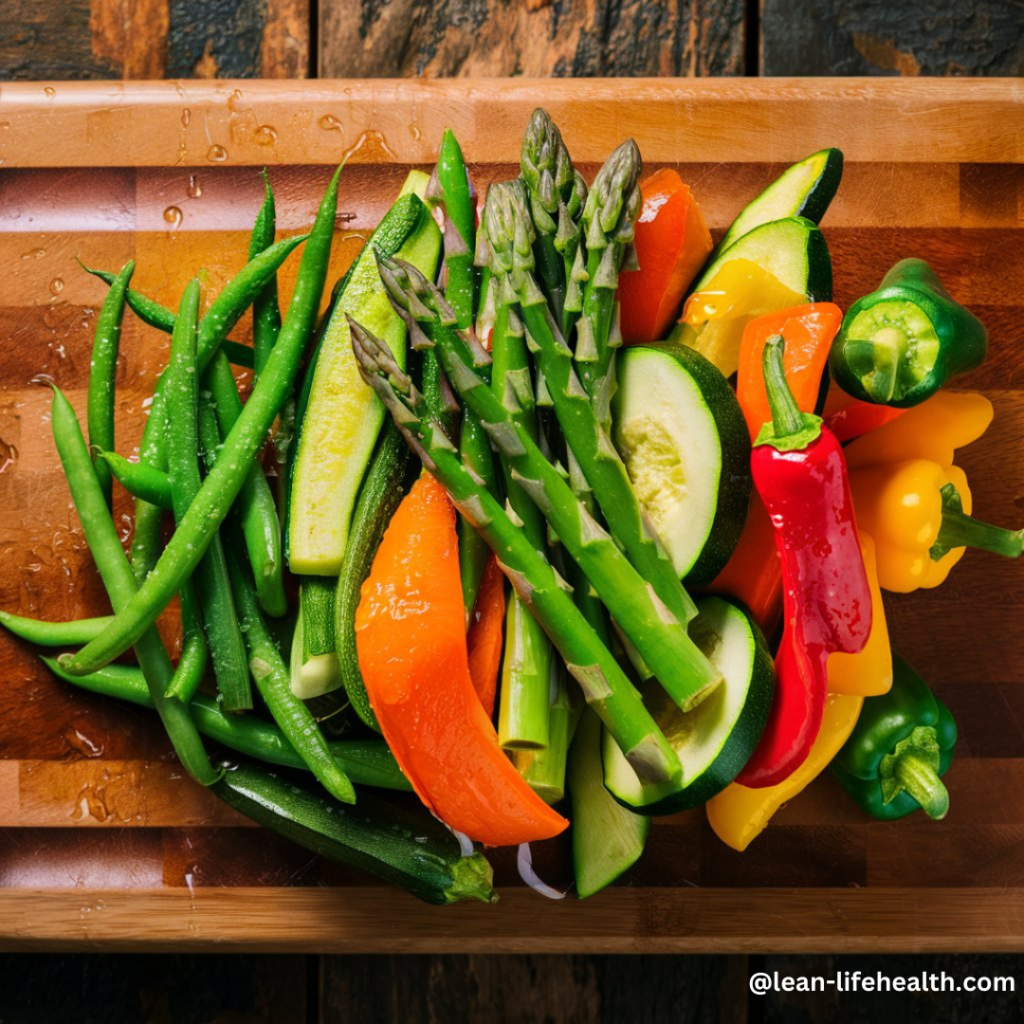

- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are excellent choices.
- Cruciferous Vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts are fiber-rich and low in carbs.
- Zucchini: A versatile vegetable that can be spiralized or used in various dishes.
- Asparagus: High in fiber and great for a variety of recipes.
- Artichokes: Particularly high in fiber, though a bit higher in carbs, they can be consumed in moderation.
Tips to Increase Fiber Intake:
- Incorporate Vegetables: Add a variety of low-carb vegetables to your meals—either raw, steamed, roasted, or in salads.
- Use Supplements: If necessary, consider fiber supplements (like psyllium husk) to boost fiber intake.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water, as fiber works best when accompanied by adequate hydration.
- Snack on Veggies: Keep raw veggies like celery, cucumber, or bell peppers on hand for healthy snacks.
By focusing on low-carb vegetables, you can increase your fiber intake and help prevent constipation while maintaining a ketogenic diet.
Long-Term Considerations
Monitor your health and adjust your diet as needed to ensure it remains balanced and sustainable.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Keto Diet
Is the Keto Diet Safe?
For most people, the keto diet is safe. However, consult your doctor before starting, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
How Long Should You Stay on the Keto Diet?
You can stay on the keto diet long-term, but it’s essential to ensure you’re getting all necessary nutrients.
Can You Build Muscle on the Keto Diet?
Yes, with adequate protein intake and strength training, you can build muscle on the keto diet.
What if I Experience a Plateau?
Adjust your calorie intake and exercise routine to overcome weight loss plateaus.
Conclusion
The keto diet offers numerous health benefits, from weight loss to improved mental clarity. By following the guidelines and tips provided, you can successfully incorporate the keto diet into your lifestyle. Give it a try and experience the positive changes for yourself!
FAQs
What is the main goal of the Keto Diet?
The main goal of the keto diet is to enter a state of ketosis, where the body burns fat for energy instead of carbohydrates.
How quickly will I see results on the Keto Diet?
Results can vary, but many people start seeing changes in weight and energy levels within the first week.
Can I drink alcohol on the Keto Diet?
Yes, but choose low-carb options like dry wine or spirits mixed with zero-carb mixers.
Is the Keto Diet suitable for everyone?
While the keto diet is beneficial for many, it’s not suitable for everyone. Consult your doctor before starting, especially if you have health conditions.
How do I maintain my weight after reaching my goal?
Gradually increase your carb intake while monitoring your weight to find a balance that maintains your results.
that maintains your results.