Introduction to Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects how your body turns food into energy. When you eat, your body breaks down most of the food into sugar (glucose) and releases it into your bloodstream. When blood sugar goes up, it signals your pancreas to release insulin. Insulin acts like a key to let the blood sugar into your body’s cells for use as energy. If you have diabetes, your body either doesn’t make enough insulin or can’t use it as well as it should. This can cause serious health issues over time.
Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This type usually develops in children and young adults, and those affected need to take insulin daily.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form, where the body doesn’t use insulin properly. Initially, the pancreas makes extra insulin, but over time it can’t keep up. This type is often linked to lifestyle factors and genetics.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and typically resolves after childbirth. However, it increases the mother’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Other Specific Types
Other specific types of diabetes result from specific genetic conditions, surgeries, medications, infections, or other illnesses.
Causes and Risk Factors
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a significant role in the development of all types of diabetes. If you have a family history of diabetes, your risk may be higher.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors such as poor diet, physical inactivity, and obesity are major risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
Symptoms of Diabetes
Common Symptoms
Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, extreme fatigue, blurry vision, and unexplained weight loss.
Type-Specific Symptoms
Type 1 diabetes symptoms can develop quickly and may include nausea, vomiting, or stomach pains. Type 2 diabetes symptoms often develop slowly over several years and can be so mild that they go unnoticed.
Diagnosing Diabetes
Blood Tests
Blood tests are essential for diagnosing diabetes. Key tests include the fasting blood sugar test, which measures blood glucose levels after an overnight fast, and the HbA1c test, which provides an average blood glucose level over the past two to three months. Another important test is the oral glucose tolerance test, which measures blood sugar levels before and after consuming a glucose-rich drink. These tests collectively help healthcare professionals determine if a person has diabetes or is at risk of developing the condition.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
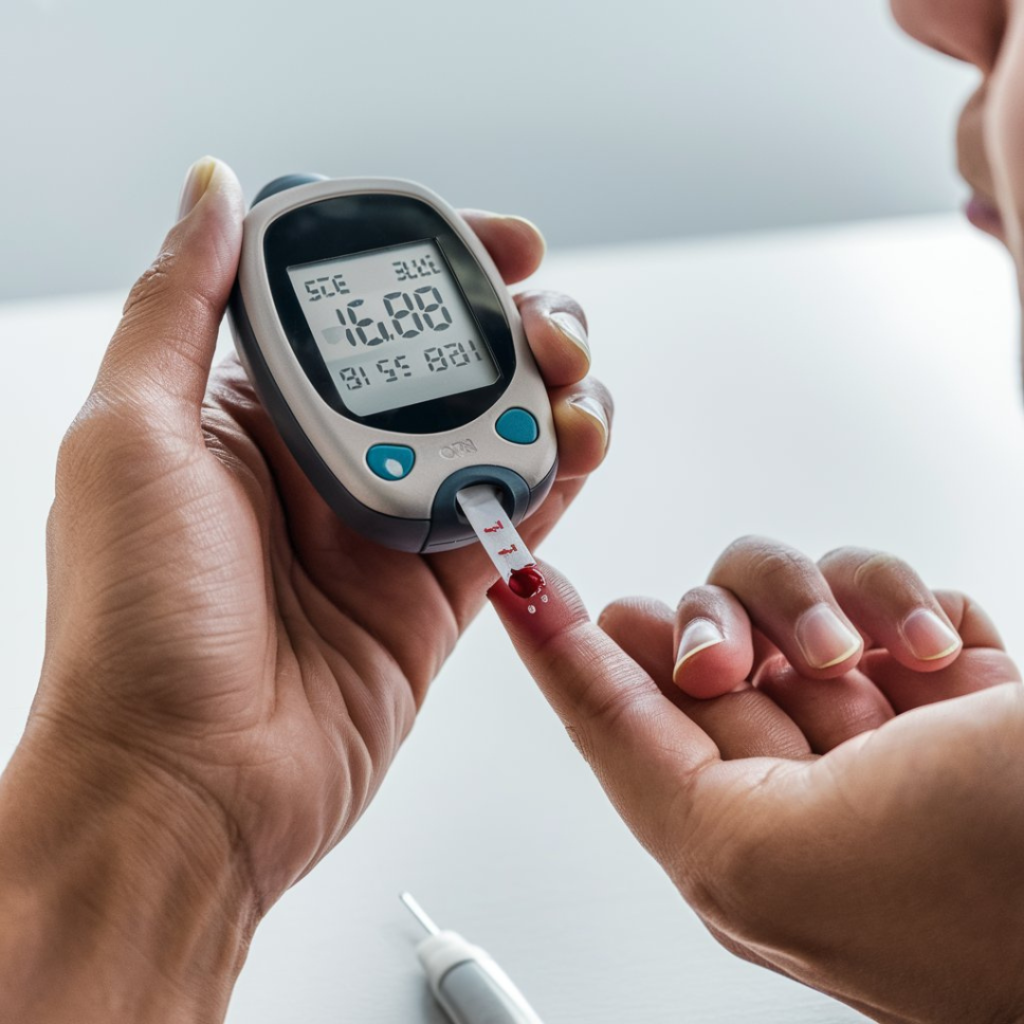

Regularly checking blood sugar levels is essential for effective diabetes management, helping to prevent complications and maintain overall health.
Complications of Diabetes
Short-Term Complications
Short-term complications include hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), and diabetic ketoacidosis.
Long-Term Complications
Long-term complications can affect major organs and lead to heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, vision loss, and nerve damage.
Managing Diabetes
Medication
Diabetes medications include oral hypoglycemic agents, which help lower blood sugar levels through various mechanisms, and injectable insulin, which is essential for managing Type 1 diabetes and some advanced cases of Type 2 diabetes. These medications are crucial for maintaining blood glucose control and preventing complications.
Insulin Therapy
Insulin therapy is crucial for individuals with Type 1 diabetes, as their bodies do not produce insulin naturally. This treatment involves administering insulin to help regulate blood sugar levels. Additionally, insulin therapy may also be necessary for those with Type 2 diabetes, particularly when other medications and lifestyle changes are not sufficient to control blood glucose levels. In both cases, insulin therapy helps manage the condition and prevent complications associated with high blood sugar.
Diet and Nutrition
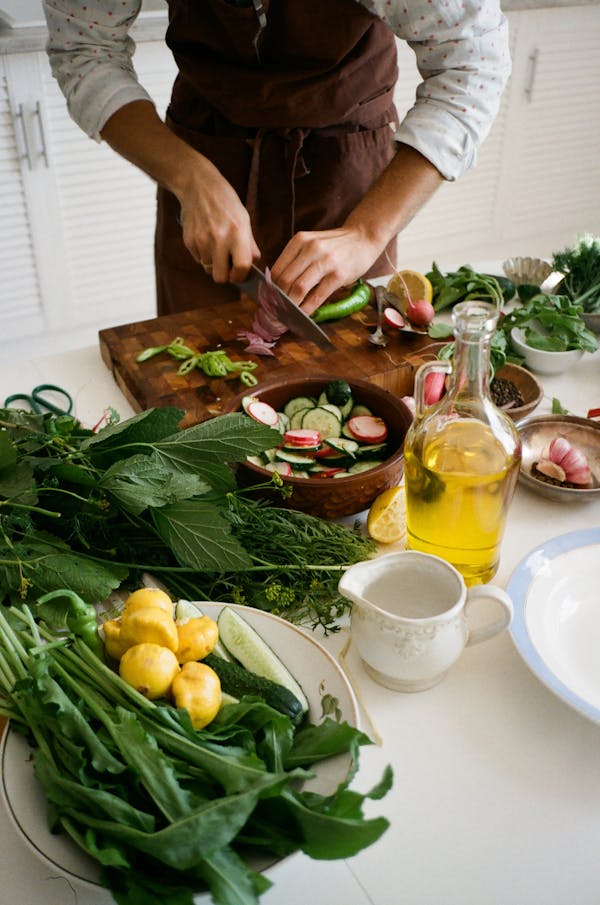

A balanced diet that includes plenty of vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains is crucial for managing diabetes. These foods help regulate blood sugar levels, provide essential nutrients, and support overall health, making it easier to control the condition and prevent complications.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is crucial for controlling blood sugar levels and improving overall health. It helps regulate glucose, supports cardiovascular health, strengthens muscles, boosts energy, and enhances mental well-being.

Blood Sugar Supplement
A blood sugar supplement is a dietary product designed to help maintain healthy blood glucose levels. These supplements often contain natural ingredients such as herbs, vitamins, and minerals that support the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar. By incorporating a blood sugar supplement into your routine, you can complement your diet and exercise efforts, potentially reducing the risk of blood sugar imbalances and promoting overall health.
Preventing Diabetes
Lifestyle Changes
Embracing a healthy lifestyle that incorporates a well-balanced diet and consistent exercise regimen can play a crucial role in substantially lowering the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes. By prioritizing nutritious food choices and engaging in regular physical activity, individuals can effectively manage their weight, improve insulin sensitivity, and enhance overall metabolic health, thereby significantly reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes and promoting long-term well-being.
Regular Screening
Regular screening for diabetes can help detect the condition early and prevent complications.
Living with Diabetes
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Living with diabetes can take an emotional toll. It’s important to seek support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends.
Support Systems
Joining a support group or community can provide valuable information and emotional support.
Innovations in Diabetes Treatment
New Medications
New medications are continuously being developed to improve diabetes management.
Technological Advances
Technological advances such as continuous glucose monitors and insulin pumps are making diabetes management easier and more effective.
Diet and Recipes for Diabetes
Healthy Eating Tips
Focusing on whole foods, avoiding processed foods, and monitoring carbohydrate intake are key strategies for maintaining optimal health. Whole foods offer essential nutrients, while avoiding processed foods reduces unhealthy fats and added sugars. Monitoring carbs helps manage blood sugar levels, especially for those with or at risk of diabetes. These practices lead to better energy, weight management, and overall health.
Diabetes-Friendly Recipes
Experimenting with diabetes-friendly recipes can make your meals both enjoyable and healthy. By trying new recipes, you can discover delicious ways to incorporate nutrient-rich ingredients that help manage blood sugar levels. This approach allows you to enjoy a variety of flavors while sticking to a diet that supports your health goals. Plus, cooking at home gives you control over the ingredients, ensuring you avoid excessive sugars and unhealthy fats. Making healthy eating enjoyable can improve your overall diet adherence and enhance your well-being.
Exercise Tips for Diabetics
Safe Exercise Practices
Consult your doctor before starting any exercise routine and choose activities that are safe and enjoyable.
Exercise Routines
Incorporate a mix of aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility exercises.
Diabetes Myths and Facts
There are many myths about diabetes, such as the misconception that eating sugar causes diabetes. Understanding the facts can help manage the condition better.
FAQs About Diabetes
- What is the main cause of diabetes?
- The main causes include genetic factors and lifestyle choices such as diet and physical activity.
- Can diabetes be cured?
- There is no cure for diabetes, but it can be managed effectively with the right treatment and lifestyle changes.
- What foods should diabetics avoid?
- Diabetics should avoid sugary foods, refined carbs, and trans fats.
- Is exercise important for managing diabetes?
- Yes, regular exercise helps control blood sugar levels and improves overall health.
- How often should diabetics check their blood sugar levels?
- This varies depending on the individual and their treatment plan, but regular monitoring is crucial.
Conclusion
Understanding diabetes is the first step toward managing and preventing it effectively. By making informed lifestyle choices and staying up-to-date with medical advancements, individuals can lead healthy and fulfilling lives despite a diabetes diagnosis.